AI agents are rapidly changing how enterprises operate. In 85 % of companies, these systems are either already in use or being deployed by the end of 2025. Businesses report improvements like a 14 % faster issue resolution and a 9 % drop in handling time per interaction in customer service. AI agents are no longer experimental. They are essential tools for managing scale, speed, and complexity. This guide explains how they work, what they offer, and how they will evolve.

What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are systems designed to act with autonomy or minimal supervision. They use machine learning to learn from data, natural language processing to interpret input, and decision-making logic to take action. Their tasks range from sending emails and handling customer questions to managing financial reports. Advanced AI agents can even collaborate on complex workflows or make decisions based on long-term data patterns.
Some agents use retrieval-augmented generation to pull from company documents and produce custom outputs. This lets them provide relevant answers based on real-time knowledge. The more advanced the agent, the more likely it includes memory, dynamic goals, and coordination with APIs or tools.
How Do AI Agents Work?
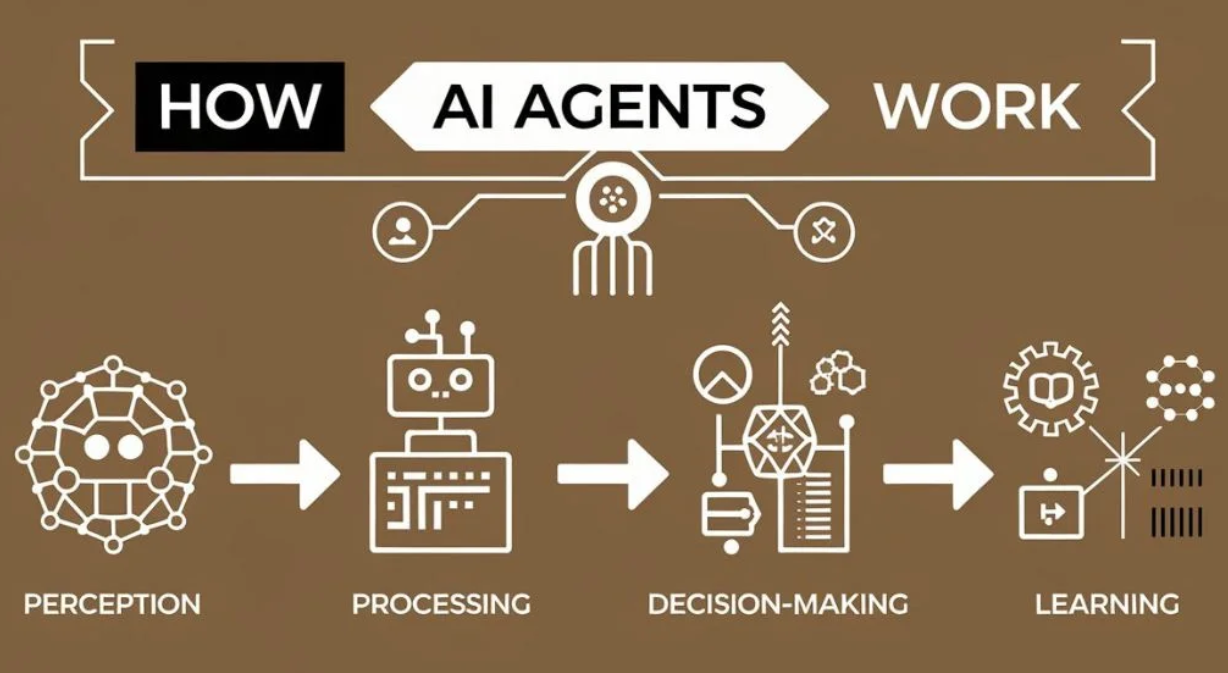
AI agents operate in cycles. First, they observe and collect data. Then, they analyze it using logic and models. They choose an action and execute it. Afterward, they assess the results and learn from feedback. This allows them to improve continuously.
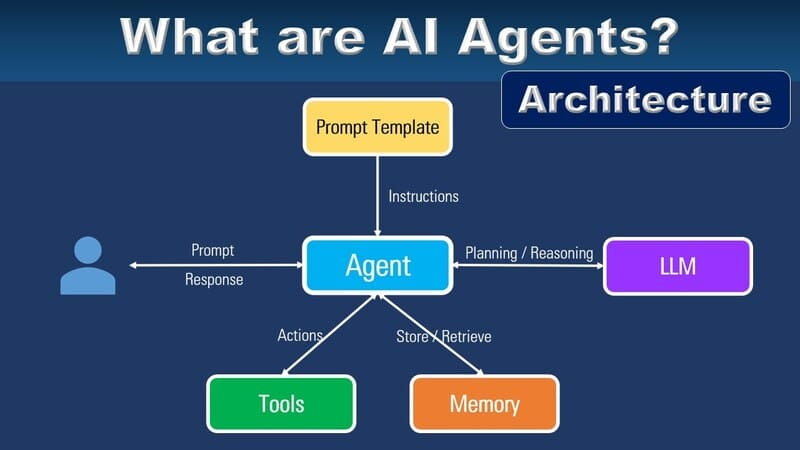
Their architecture includes a language model, a retrieval system, an execution core, and a feedback loop. Some use protocols like Model Context Protocol to manage tool access and permissions safely. These agents often sit on top of your stack, interacting with APIs, documents, databases, or cloud tools.
For instance, the Graphlogic Generative AI & Conversational Platform connects agents to CRMs or knowledge bases with API support. The Graphlogic Text-to-Speech API lets them respond in human-like voices during real-time conversations.
Key Features of AI Agents for Enterprises
Enterprise-grade AI agents must meet several standards. They should automate tasks at scale with high accuracy. They need to process input and deliver responses in real time. Seamless integration with ERP, CRM, and messaging systems is critical. Agents must be modular so logic can be updated quickly.
Transparency is another key feature. Businesses need logs of every decision agents make, along with explainable reasoning. This is especially important for regulated industries.
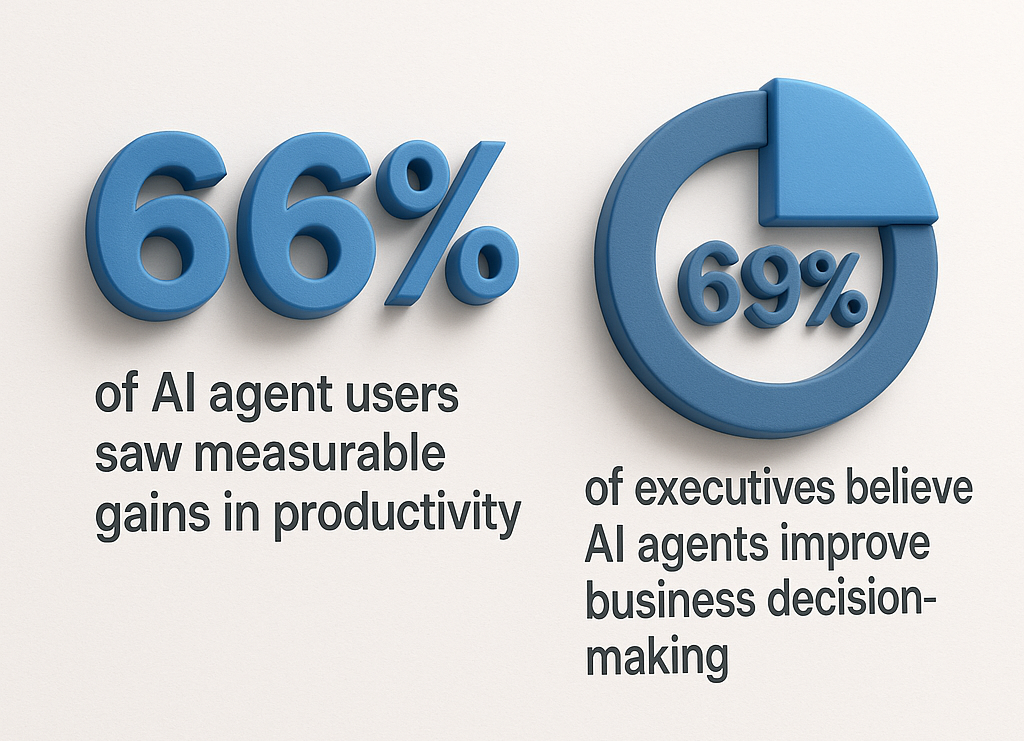
According to PwC, 66 % of AI agent users saw measurable gains in productivity. IBM reports that 69 % of executives believe AI agents improve business decision-making.
Benefits of Using AI Agents in Business
AI agents are becoming a natural and helpful part of how companies work. In contact centers, they help more customer issues get solved on the first try and make everyday tasks quicker. This means teams can support more people without needing to grow the team, even during busy times or unexpected spikes in demand.
Behind the scenes, AI quietly handles repetitive work like checking invoices, managing IT tickets, or handling basic internal requests. It works without breaks, makes fewer mistakes, and can even notice small errors or unusual patterns that people might miss. This makes processes not just faster but more dependable.
For customers, the experience feels easier. They get help any time of day, without long waits, and the answers feel more personal because AI can remember past conversations, pick up on tone, and respond in a way that fits the moment. AI also helps teams notice patterns and problems early that wouldn’t always show up in normal reports.
One of the biggest benefits is how it supports people. By taking over the repetitive or routine work, AI gives employees more time to focus on tasks that need creativity, care, or real judgment. It’s not about replacing people but helping them spend their time where it matters most.
Real World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are everywhere now. In customer support, they handle up to 80 % of routine queries. In logistics, agents optimize delivery schedules and warehouse planning. In marketing, they adjust campaigns in real time based on customer behavior.
In the finance sector, agents process transactions, verify invoices, and flag anomalies. Some companies cut their financial reporting time by 40 %, while reducing errors by 94 % through agent-driven tools. At Siemens, agents help detect early signs of equipment failure and cut downtime by 25 %.
In software development, 82 % of companies now use coding agents for code suggestions, reviews, or testing. However, only 8 % use them for full code deployment due to quality concerns.
Challenges of Implementing AI Agents
Deploying agents is not simple. Data privacy is a key issue. 53 % of companies cite this as their top concern. Other challenges include integration with legacy systems and lack of employee trust.
Some developers report frustration with agent output. According to ITPro, 46 % of developers do not trust AI output, and many spend extra time verifying results.
Security is another major issue. 96 % of tech professionals expect AI agents to introduce new threats. Over 23 % have already seen incidents involving data exposure or misuse by agents.
Future Trends in AI Agents for Enterprises
AI agents are not static tools. The next two to five years will bring massive changes in how they behave and what they can do. Here are the major shifts already taking shape.
- More personalized and adaptive agents
Agents will begin adapting tone, content, and strategy to individual user preferences. This means not just adjusting language but modifying workflows based on behavior patterns. Expect customer-facing agents that learn to speak differently to loyal clients than to new users. Internally, agents will adapt to how specific departments operate. - Multi-agent collaboration
The future will be built on networks of agents working together. Rather than single agents doing everything, specialized agents will coordinate tasks. For example, one agent could gather data, another could analyze it, and a third could present it in a dashboard. This modular setup mirrors how human teams work and improves performance and speed. Salesforce and other major tech firms are already experimenting with such frameworks. - Voice-first and multimodal agents
With the rise of voice interfaces and wearable tech, agents will increasingly operate through speech. The Graphlogic Text-to-Speech API enables agents to speak fluidly. Combine that with natural language understanding, and you get full voice assistants that can run workflows in healthcare, field services, and support without screens. Multimodal agents will also process text, images, and voice simultaneously, creating richer interaction models. - No-code agent builders
Enterprises want agility. No-code and low-code agent builders will enable teams to create and launch agents without developer input. This democratizes AI and shifts power to business units. Expect major platforms to integrate drag-and-drop agent builders with governance controls. - Federated agent ecosystems
In the next stage of evolution, organizations will deploy agents that cooperate across company boundaries. For example, a supplier’s agent might sync with a retailer’s system to update stock levels or automate invoicing. This type of cross-organization orchestration will require common standards, secure identity layers, and clear data governance protocols. - Ethical and regulatory frameworks
As agents gain autonomy, governments and regulators will step in. We are already seeing draft laws that define accountability and transparency rules for agents in the EU and US. Companies that do not proactively implement audit trails and bias controls will face compliance issues. - Autonomous agents with long-term memory
Future agents will not just respond to input. They will set and pursue long-term goals. With built-in memory, they will track project context, adapt to user feedback, and refine strategies over weeks or months. This shift requires new ways to evaluate performance and risk. - Embedded agents in everyday software
Agents will not live in separate platforms. They will be embedded directly into tools like Excel, Slack, Gmail, or Notion. These micro-agents will help users write, plan, analyze, and execute tasks faster with fewer manual steps. - Cloud-native orchestration and governance tools
To manage agent sprawl, we will see the rise of orchestration dashboards. These tools let IT teams monitor activity, assign permissions, and track decisions made by agents. Expect this to become a critical layer in enterprise AI governance by 2026.
Key Points to Remember About AI Agents
- AI agents automate tasks and adapt to input using machine learning and logic
- Enterprises see cost, time, and efficiency gains in support, operations, and finance
- 85 % of large organizations already use or plan to deploy agents in 2025
- Major benefits include faster service, reduced error, and deeper insights
- Risks include data privacy breaches, poor output quality, and governance gaps
The next evolution includes multimodal interaction, long-term memory, and multi-agent collaboration
FAQ
An AI agent is a software system that can take action based on data and instructions. It uses language understanding, logic, and memory to complete tasks automatically.
They automate work, reduce costs, improve accuracy, and deliver services faster. Many companies achieve ROI in under a year.
Tasks range from answering support tickets to processing invoices, summarizing reports, analyzing data, and even helping in software testing.
They can be secure if well managed. Risks increase when agents are given tool access without governance. Proper permissioning, logging, and auditing are essential.
Begin with narrow, well-defined tasks. Use platforms like the Graphlogic Generative AI & Conversational Platform that offer integration and control features. Monitor results closely and expand based on clear outcomes.

