In 2025, AI chat tools have become foundational across industries. ChatGPT now serves 700 million weekly users. It handles 2.5 billion prompts daily, marking its role as indispensable in both consumer and professional spaces. This rapid adoption raises important questions about how these tools work and when each type serves us best. As a medical technology expert, I see ethical and practical implications daily v from patient communication to misinformation risks. Now is the moment for clear distinction, evidence and direction.

What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot operates with rule-based logic, matching inputs to fixed responses. It cannot adapt or remember prior interactions. Yet they are widely used v from booking appointments in clinics to triaging basic health queries. Accuracy depends on script coverage, which means they fail when users stray outside those patterns. Use cases include pharmacy opening hours or simple symptom checks. I recommend adding transparent guidance about scope and providing a human fallback. Recent data show 800 million weekly active users rely heavily on these systems for predictable assistance. This longevity and reliance can build both efficiency and trust v if handled responsibly.
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI extends far beyond fixed dialogue. It uses NLP, machine learning and context tracking. It adapts as conversations unfold and learns from past exchanges. The global conversational AI market was valued at $11.58 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach $41.39 billion by 2030. In healthcare, this allows for personalized triage, follow-up questions, and multilingual support. Enhancing voice interfaces with tools like Graphlogic Text-to-Speech API offers better accessibility. Employers should ensure these systems are explainable, auditable and ethically deployed to avoid bias or overreliance.
Key Differences Between Chatbots and Conversational AI
Rule-based chatbots are built for predictable, repetitive scenarios. They operate by matching user input to pre-written responses. This makes them reliable for consistent answers but limits them when the conversation changes direction or includes unexpected topics. They are best when you need speed and cost control, but they cannot adapt to new information without manual reprogramming.
Conversational AI goes further. It interprets nuance, understands intent, and maintains context across multiple exchanges. This means it can respond appropriately when a user changes the subject, provides extra detail, or expresses emotion. It can manage multi-step processes such as completing a form while answering clarifying questions in real time. Its adaptability allows it to scale across different platforms, languages, and industries with far less manual intervention than a chatbot.
The distinction becomes critical in high-stakes areas such as medical intake, legal consultations, or emotional support services. For example, a chatbot might confirm a patient’s appointment, but it would fail to understand if a patient casually mentions new symptoms in the same conversation. Conversational AI could detect those symptoms, adjust its response, and either gather more information or escalate the case to a clinician.
A good practice for businesses is to evaluate their interaction complexity and error tolerance before deciding which tool to deploy. In some cases, combining both is the most cost-effective option—using chatbots for initial screening and conversational AI for deeper engagement.
Comparison Table: Chatbots vs Conversational AI
| Feature | Chatbots | Conversational AI |
| Interaction Style | Pre-programmed, rule-based replies | Contextual, adaptive, human-like |
| Learning Capability | None without manual updates | Learns and improves over time via AI models |
| Complexity Handling | Handles only simple and predefined queries | Manages complex, multi-turn, and evolving dialogues |
| Personalization | Limited to scripted personalization | Tailors responses using user history and preferences |
| Deployment Speed | Fast, often within days | Slower due to training and integration needs |
| Scalability | Requires manual scripting for each new case | Expands to new domains with minimal manual input |
| Best Use Cases | FAQs, appointment booking, basic service automation | Customer support, triage, advanced advisory roles |
| Maintenance | Low technical requirements | Continuous monitoring, training, and updates needed |
| Cost Profile | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial investment but potentially greater ROI |
When to Use a Chatbot
A chatbot is the smart choice when your communication needs are narrow, repetitive, and clearly defined. It works best in situations where the user questions are predictable and can be answered from a fixed knowledge base. Examples include sending reminder messages for upcoming appointments, handling basic FAQs about service hours or policies, or providing simple instructions such as how to reset a password.
Deployment is usually quick and often achievable within a few days. The budget requirements are modest compared to more advanced solutions. For teams that handle high volumes of repetitive queries, such as appointment confirmations, store location directions, or order status updates, a chatbot can save many work hours every week. This efficiency frees human staff to focus on cases that require judgment or empathy.
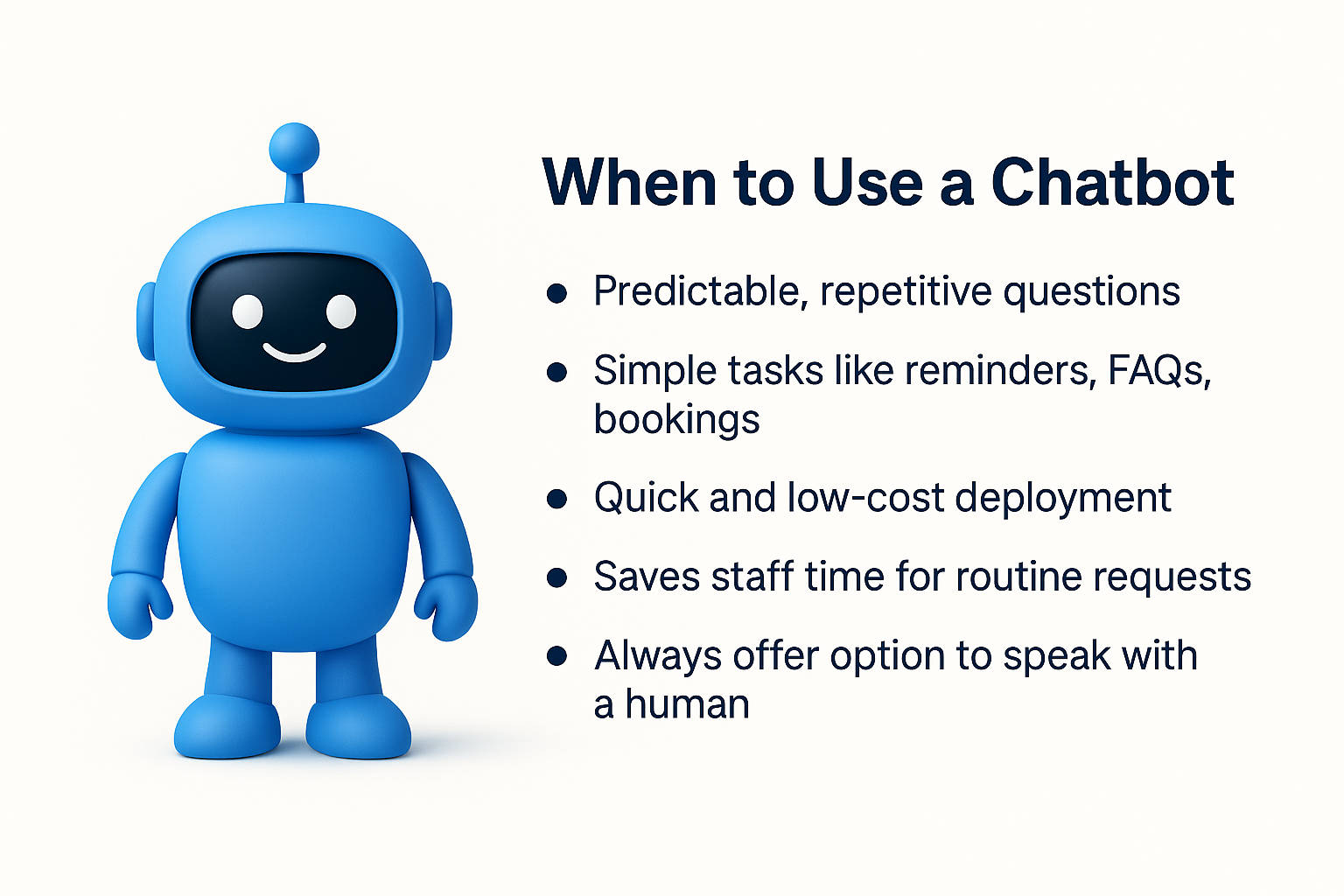
To maximize value, always include a clearly visible option to connect with a human representative. Clearly stating the chatbot’s scope at the start of the conversation helps manage expectations and prevents frustration when a question falls outside its capabilities. In sectors such as healthcare or banking, this transparency is important for maintaining trust.
When to Use Conversational AI
Conversational AI is most effective when personalization, contextual understanding, and conversational depth are important. It works well in scenarios such as medical symptom triage that develop over several exchanges, where the AI needs to ask follow-up questions based on prior responses. When users shift topics, add detailed information, or change tone in the middle of a conversation, conversational AI can adjust in real time.
It scales across multiple platforms, including web chat, mobile applications, and voice systems, and across languages. This makes it possible to provide consistent service worldwide. In large hospitals, telehealth networks, or service companies with many branches, conversational AI can handle complex routing, connect with back-end systems, and keep a record of previous interactions to ensure continuity of service.

In healthcare, for example, a patient may begin by asking about a prescription and later mention new symptoms. A conversational AI can detect this change in context, ask clarifying questions, and escalate the case to a clinician if necessary. Over time it adapts, remembers patterns, and refines its performance, which results in higher quality service and stronger user trust.
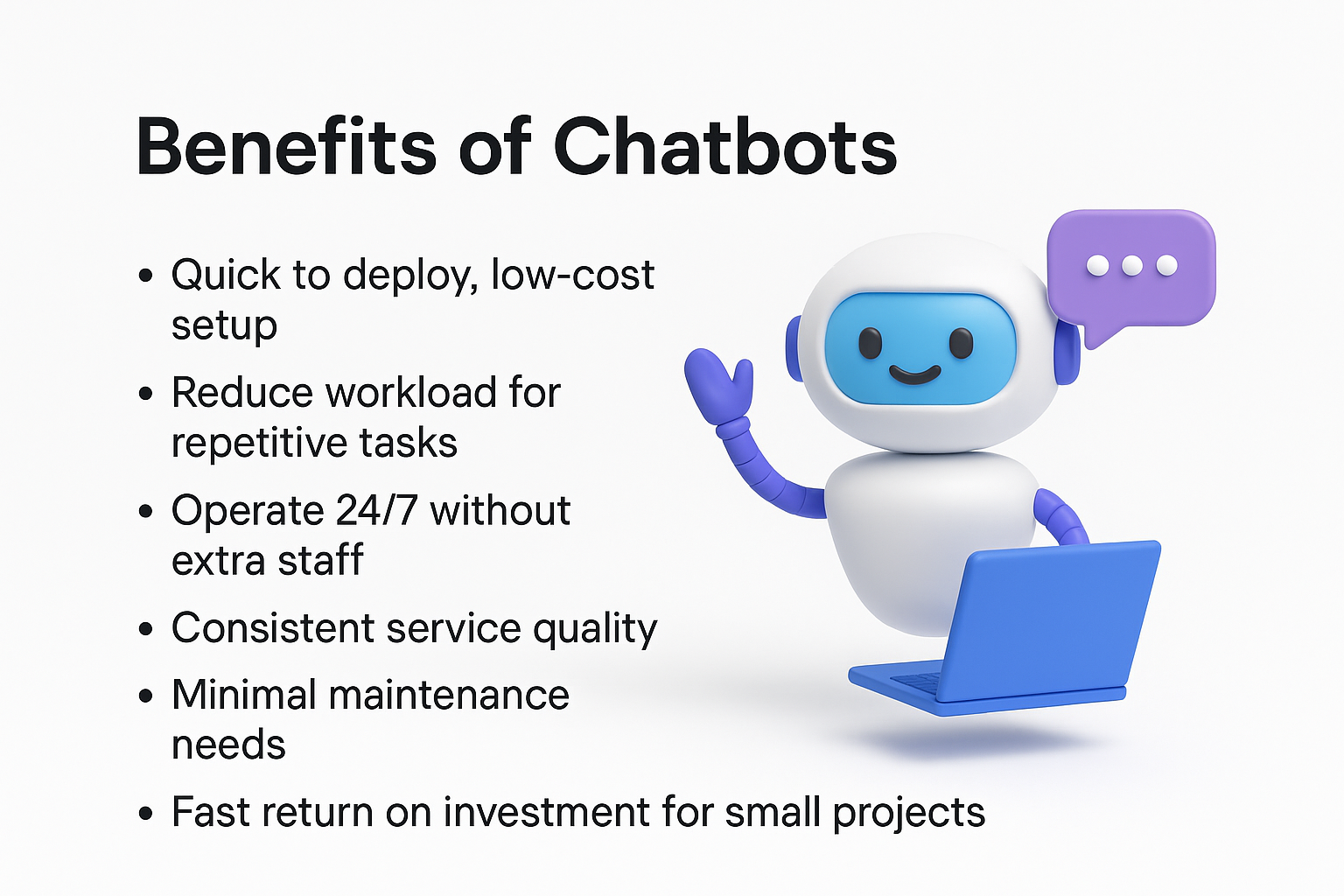
Benefits of Chatbots
Chatbots are quick to deploy and require a relatively low investment. They reduce the workload for repetitive tasks and can operate outside regular business hours without additional staffing costs.
Their reliability in handling predefined workflows ensures consistent service quality. For example, in a medical clinic, a chatbot can manage appointment booking or send pre-visit instructions without the risk of human error caused by fatigue. Maintenance needs are minimal, and updating the knowledge base can often be done without advanced technical skills.
For pilot projects or workflows with a narrow scope, chatbots can deliver a fast return on investment. When combined with clear user expectations and transparent communication, they act as efficient and cost-effective virtual assistants that help maintain service quality at scale.
Benefits of Conversational AI
Conversational AI enables richer and more engaging interactions that go beyond simple transactions. It can access and integrate with patient data, historical records, or appointment scheduling systems to provide contextually relevant responses. This makes it possible to offer proactive reminders, tailored recommendations, and adaptive support.
Using tools such as the Graphlogic Text-to-Speech API improves accessibility for users with low vision, reading difficulties, or language barriers. Conversational AI systems learn continuously from past interactions, which allows them to reduce points of friction over time and create smoother experiences.
This adaptability supports a wide range of workflows, from financial assistance and billing inquiries to symptom triage and emotional coaching. When well designed and implemented, conversational AI provides a human-like experience that can handle large-scale service demands without losing empathy.
Challenges of Implementing Chatbots
Chatbots are limited because they rely on pre-programmed scripts. When a conversation moves beyond the programmed scope, they cannot adapt. This can lead to user frustration and a feeling of being trapped in an automated loop.
Expanding a chatbot to cover more topics or services requires creating many new scripts manually, which can be time-consuming. Without careful planning, users may find the experience impersonal, especially in sensitive contexts such as healthcare or customer complaints.
To prevent these problems, organizations should include clear messaging at the beginning of interactions, such as informing the user that they can speak to a human agent for complex issues. Providing an easy route to human assistance improves the overall experience.
Challenges of Implementing Conversational AI
Conversational AI requires a higher initial investment in technology, data infrastructure, and training. Implementation often involves connecting with multiple systems and ensuring compliance with privacy laws, especially in industries like healthcare and finance.
Risks include bias, inaccurate responses, and the possibility of misinformation. Without oversight, these systems may produce harmful or misleading information. Transparency and explainability are essential, and operators should be able to understand why a system gave a certain answer.
Staff training is critical. Employees need to know how to monitor the system, understand its limitations, and take over when required. Regular monitoring and updates are necessary to maintain accuracy, ethics, and trust.
Real-World Examples
In retail, chatbots are often used to provide quick answers about order status, delivery times, or store opening hours. These systems reduce the load on call centers and ensure customers get instant responses at any time of day. They are also used in loyalty programs to inform shoppers about available points, discounts, or personalized offers.
In healthcare, chatbots can handle appointment reminders, send preparation instructions before a medical visit, or provide directions to a clinic. They can also offer quick responses to common patient questions, such as what documents to bring or how to access laboratory results.
Conversational AI expands these capabilities significantly. In clinical settings it can triage symptoms, ask clarifying questions, and escalate urgent cases directly to medical staff. For example, if a patient reports chest discomfort during a virtual interaction, conversational AI can identify the potential seriousness of the symptom and guide the patient toward immediate care while alerting a healthcare professional.
Large hospitals and telemedicine platforms in 2025 report using conversational AI for triage at a scale involving hundreds of millions of patient interactions annually. These solutions, when implemented with rigorous safety checks, improve access to care, shorten wait times, and support more personalized patient communication. They also help restore a sense of empathy in large-scale healthcare systems by ensuring that serious cases are prioritized quickly and that routine cases are handled efficiently.

How to Choose Between Them
Start by mapping query complexity and volume. Assess budget, data infrastructure and user demographics. If needs are direct and repeatable, choose a chatbot. If nuance, empathy or memory matter, conversational AI delivers long-term value. Build a small pilot, test with real users, monitor satisfaction, fallback rates, error patterns. Scale gradually with safeguards, audit logs and human-in-loop oversight.
Key Points to Remember
- Chatbots follow fixed rules
• Conversational AI understands context and adapts
• Chatbots are quick and inexpensive
• Conversational AI costs more but personalizes and scales
FAQ
Chatbots use fixed scripts. Conversational AI understands context, intent and adapts.
Only with a full redesign, adding context memory, NLP training and infrastructure.
They can help when used carefully. You must supervise responses, validate critical replies and train staff in oversight.
Around 700 million weekly users now rely on ChatGPT. It processes 2.5 billion prompts per day.