An enterprise chatbot is an AI tool that helps large organizations automate service, internal communication, and data workflows. It connects with CRMs, ERPs, and HR systems to manage processes and reduce manual work.
By 2025, such systems have become standard in business operations. According to McKinsey’s State of AI in 2024 report, 65% of companies now use AI in daily work, and 40% plan to increase investments in automation.
Modern chatbots rely on large language models to understand intent, context, and tone. Many now support text, voice, and image input, making them central to enterprise digital strategies.
In this article, we’ll look at the main types of enterprise chatbots, their key benefits, real-world examples, and how companies can choose and implement them effectively.

Types of Enterprise Chatbots
Enterprise chatbots fall into three main categories:
- Rule-based chatbots
- AI-powered chatbots
- Hybrid chatbots
Each type supports different business goals depending on process complexity, data flow, and user expectations. The choice usually depends on how much flexibility and learning a company needs.
Rule-Based Chatbots
Rule-based chatbots rely on predefined commands, buttons, and decision trees. They respond to keywords or follow step-by-step menus. These bots are effective when tasks are simple and predictable — such as answering FAQs, tracking orders, or booking appointments.
They work well in structured environments like logistics, healthcare scheduling, or retail delivery updates. For example, a clinic might use such a bot to confirm appointments or share lab results but not to interpret medical questions.
Their biggest advantage is reliability. They always give consistent answers and require minimal maintenance. The drawback is rigidity — they can’t handle context, slang, or emotional language.
A study in Frontiers in Digital Health (2023) showed that rule-based chatbots reduced response time by 30%, yet failed in 25% of cases when users used informal expressions.
Rule-based systems remain relevant in 2025 for regulated sectors that value control and compliance over flexibility.
AI-Powered Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots use natural language processing and machine learning to analyze intent, context, and sentiment. They learn from past conversations and improve accuracy over time. Unlike rule-based bots, they can interpret open questions, multiturn dialogue, and even detect emotion.
These systems are now common in healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and education. In medicine, AI chatbots can guide users through symptom checks and refer them to specialists following the WHO’s 2021 report on AI in Health.
In business, AI-powered bots help customers troubleshoot issues, manage orders, and access real-time data from integrated systems. They also support internal functions like HR helpdesks and IT support by understanding natural language requests.
Many enterprises use scalable platforms like the Graphlogic Generative AI & Conversational Platform. It combines generative AI, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and data governance, making chatbots accurate, multilingual, and compliant with corporate standards.
In 2025, AI-powered bots increasingly use multimodal inputs — text, voice, and image — creating smoother and more natural conversations. They form the backbone of enterprise automation and customer experience strategies.
Hybrid Chatbots
Hybrid chatbots combine the best of both worlds. They use rule-based logic for simple interactions and AI models for complex ones. This dual setup ensures both speed and adaptability.
For example, a hybrid chatbot in banking may handle basic account queries through pre-set rules but rely on AI for personalized financial advice. In healthcare, it can follow strict protocols for medical disclaimers while using AI to explain test results in plain language.
This mix helps organizations maintain control where it’s needed while allowing AI to manage context and tone. It’s also cost-efficient — only part of the system requires training and computation.
In 2025, hybrid chatbots are becoming the default architecture for most enterprises. They provide the right balance between compliance, flexibility, and performance — ideal for organizations scaling their AI capabilities gradually.
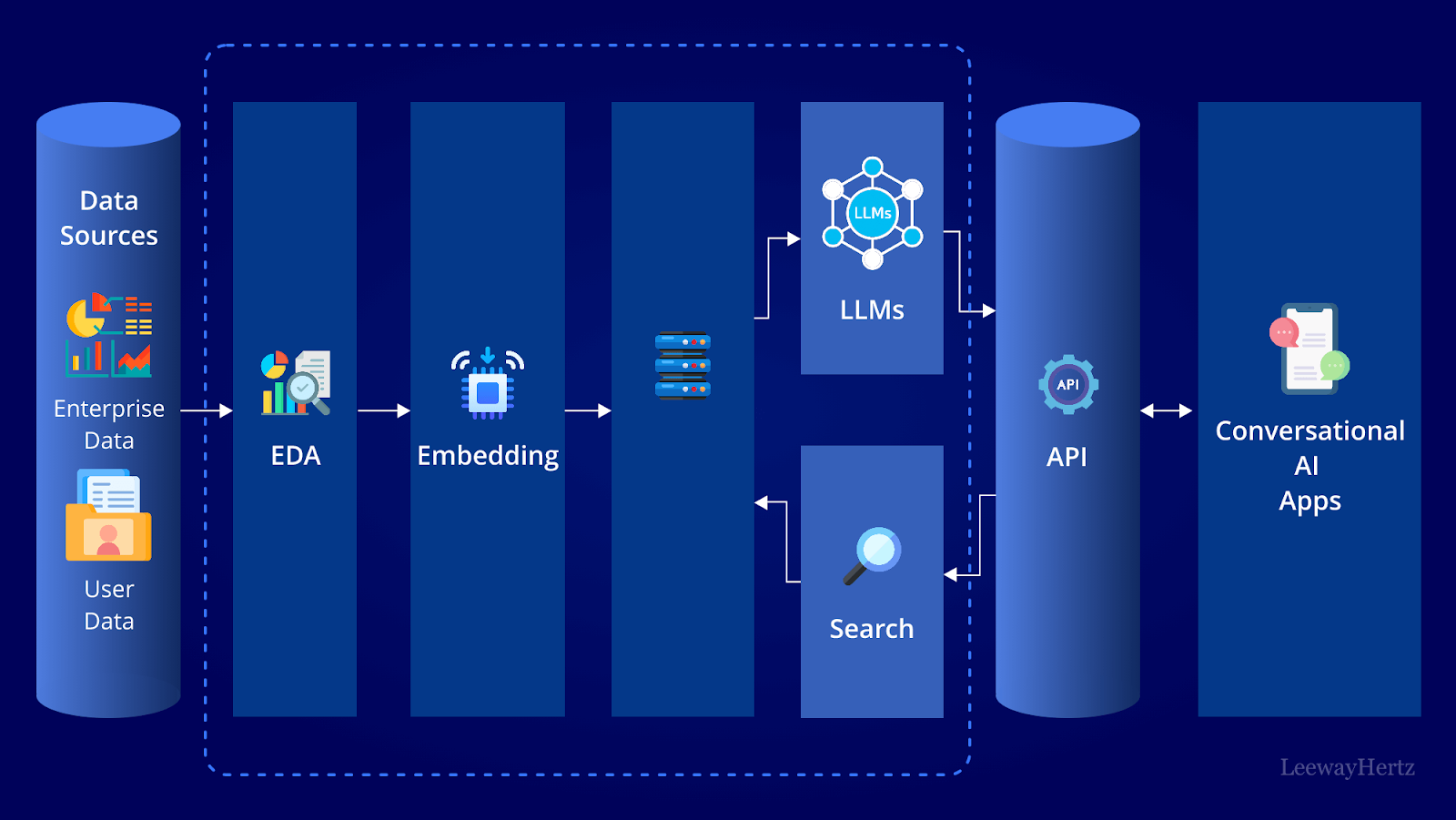
Key Benefits of Enterprise Chatbots
Enterprise chatbots now play a central role in digital operations. They deliver measurable results in productivity, customer satisfaction, and cost reduction. By 2025, most large organizations treat chatbots not as optional tools but as a core part of their communication and automation strategy.
The main benefits include:
- Faster and more personalized customer responses
- Improved operational efficiency across departments
- Scalable communication for global teams and users
- Data-driven insights that support better decision-making
Enhancing Customer Service
Customer experience remains the top reason companies adopt chatbots. Modern chatbots provide 24/7 support, answer repetitive questions, and route complex cases to human agents. This reduces wait times and improves user satisfaction.
According to Gartner’s Customer Experience Forecast 2024, 80% of service organizations will shift from mobile apps to conversational interfaces by 2025. This transition is driven by user preference for natural, fast, and context-aware communication.
AI-powered chatbots also allow more personal interaction. They can analyze user history, sentiment, and behavior to tailor responses. This helps brands maintain a consistent tone and style across digital channels.
Voice is becoming an integral part of this shift. With APIs such as the Graphlogic Text-to-Speech API, enterprises can turn text replies into natural, multilingual voices. This is especially important for healthcare, finance, and education, where accessibility and accuracy matter. Voice chatbots make digital support more human and inclusive, helping users who prefer listening over reading.
Streamlining Internal Operations
Chatbots now play an equally important role inside organizations. They automate routine HR, IT, and administrative requests, which frees up time for teams to focus on strategic work.
Employees can ask about vacation policies, request documents, or reset passwords directly in chat. The bot retrieves information instantly, cutting the need for emails or service tickets.
A Deloitte AI Operations Report 2024 found that internal chatbots reduce administrative costs by up to 30% and improve employee satisfaction by 20%. This gain comes from faster responses, fewer manual errors, and consistent information across systems.
Chatbots also improve onboarding and training. New employees can use an internal assistant to learn company policies, access tools, or schedule meetings without depending on HR. In larger enterprises, AI assistants now integrate with collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams, providing real-time guidance and analytics.
By reducing repetitive work and improving access to knowledge, enterprise chatbots help organizations operate more efficiently, scale globally, and maintain agility even in complex environments.
Real-World Examples of Enterprise Chatbots
By 2025, enterprise chatbots have moved far beyond experimental pilots. They now handle millions of customer interactions daily, support internal teams, and generate measurable business outcomes. The following examples show how different industries use conversational AI to achieve specific goals — from improving customer experience to optimizing complex workflows.
Sephora’s Virtual Assistant
Sephora has been one of the early adopters of conversational AI in retail. Its chatbot helps users find products, match shades, and learn makeup techniques through guided conversations. It also sets restock reminders and connects users to beauty consultants when needed.
The assistant uses purchase history and browsing data to create personalized recommendations. It can identify user preferences such as skin tone, product texture, or price range and suggest new items dynamically.
By 2025, Sephora’s chatbot has become part of a wider AI ecosystem that integrates the company’s e-commerce platform, loyalty program, and virtual try-on tools. This ecosystem allows customers to get consistent guidance across web, mobile, and in-store experiences.
According to Sephora’s internal 2024 innovation report, conversational AI increased repeat purchases by 18% and reduced average response time by 40%. The success of this approach shows how personalization at scale can strengthen both brand loyalty and operational efficiency.
Bank of America’s Erica
Erica is one of the most advanced enterprise chatbots in the financial industry. Developed by Bank of America, it serves as a digital financial assistant available 24/7 within the bank’s mobile app.
Erica helps customers check balances, manage transactions, schedule payments, and analyze spending patterns. It also provides proactive alerts — for example, when a bill is due or an unusual transaction occurs.
Since its launch, Erica has handled more than 1.5 billion interactions, according to the Bank of America newsroom. The chatbot now uses natural language understanding and predictive analytics to identify financial trends for users, helping them make better budgeting decisions.
In 2025, Erica’s updates include generative AI modules that explain complex terms or summarize statements in plain language. This helps improve financial literacy among users while keeping customer support costs low. Bank of America reports that chatbot-driven automation has reduced routine service calls by more than 25%, freeing up agents to handle high-value interactions.
Other Notable Implementations
Several other enterprises have demonstrated how conversational AI scales across sectors:
- KLM Royal Dutch Airlines uses chatbots to manage flight updates, rebookings, and passenger support across multiple messaging platforms.
- Mayo Clinic employs AI assistants for triage and patient education, using medical NLP systems aligned with clinical safety standards.
- H&M integrates conversational commerce to help users find products, track orders, and access sustainability data.
These cases show how enterprise chatbots have evolved from simple support tools into intelligent communication systems. They connect users to data, automate processes, and create a seamless bridge between humans and technology — a defining feature of digital business in 2025.
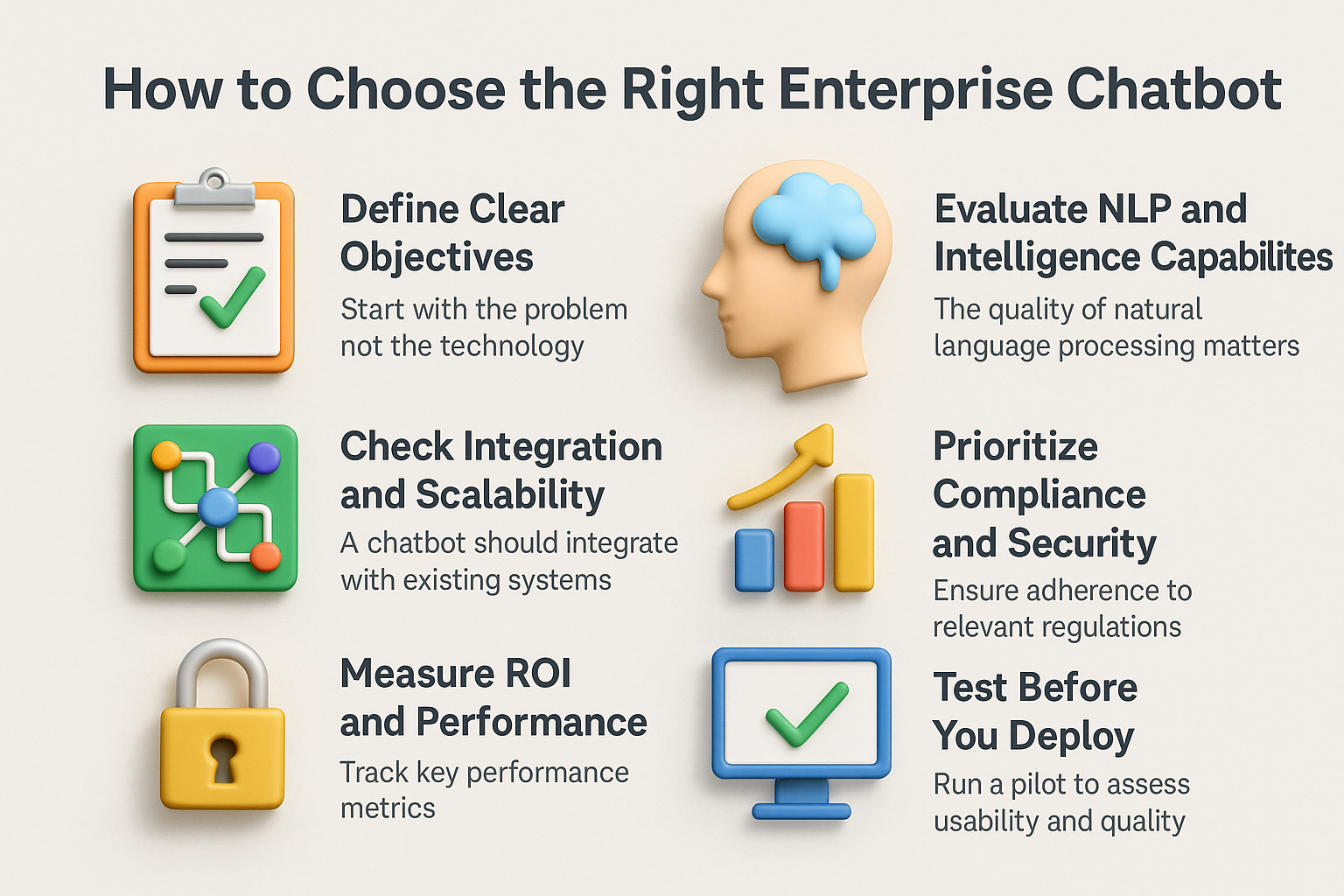
How to Choose the Right Enterprise Chatbot
Choosing the right enterprise chatbot in 2025 means balancing technology, usability, and long-term value. The market has matured — there are hundreds of chatbot platforms, from simple rule-based tools to advanced multimodal AI systems. Selecting the right one depends on your goals, integration needs, and data protection requirements.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start with the problem, not the technology.
Do you need a chatbot to improve customer service, automate internal requests, or support sales?
Defining a primary goal helps narrow down platforms and avoid overpaying for features you won’t use.
It’s also helpful to map your audience. Internal users (employees) have different expectations than customers. Internal bots must be accurate and secure, while customer-facing ones should emphasize tone, accessibility, and brand consistency.
2. Evaluate NLP and Intelligence Capabilities
The quality of natural language processing (NLP) determines how well a chatbot understands intent, slang, and emotional cues.
Modern enterprise systems rely on large language models fine-tuned for specific industries, from finance to healthcare.
Ask vendors about:
- Language coverage and accuracy rates
- Sentiment analysis capabilities
- Support for multimodal input (text, voice, image)
- Data training methods and update frequency
If your business operates in multilingual regions, ensure the chatbot supports context switching between languages without losing accuracy.
3. Check Integration and Scalability
A chatbot should integrate easily with your existing systems — CRM, ERP, HR, and analytics platforms. Integration allows it to access real-time data and automate end-to-end workflows instead of working in isolation.
Look for solutions that provide REST or GraphQL APIs, SSO support, and connectors for tools like Salesforce, SAP, or Microsoft 365.
Scalability also matters: the system should handle peak loads and multiple channels (web, app, social media, voice).
Enterprises often run proof-of-concept projects to test scalability under simulated workloads before full deployment.
4. Prioritize Compliance and Security
Data protection has become a central factor in chatbot adoption.
If you handle sensitive data — for example, in healthcare, banking, or public services — ensure the chatbot complies with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO/IEC 27001.
Check encryption standards, data residency options, and user consent mechanisms. Modern enterprise chatbots should include role-based access control, logging, and audit capabilities.
5. Measure ROI and Performance
A well-designed chatbot should pay off within 6 to 12 months. Track key performance metrics such as:
- Response accuracy
- Resolution rate
- Cost savings per interaction
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT)
- Employee productivity gains
Comparing these indicators before and after deployment helps justify investment and plan scaling.
6. Test Before You Deploy
Most enterprise providers offer pilot programs or demos. Testing allows you to evaluate usability, integration, and response quality before committing long-term.
Tools like the Graphlogic Virtual Avatars provide an interactive way to simulate real conversations and assess how human-like communication can improve customer training, support, or telehealth experiences.
A short trial with real users — even in a single department — often reveals more than a long technical evaluation.
By approaching chatbot selection as a strategic decision rather than a quick deployment, enterprises can ensure the system fits their needs, scales effectively, and remains compliant with future AI regulations.
Challenges of Implementing Enterprise Chatbots
Implementing enterprise chatbots can be complex. The main issues involve system integration, conversation quality, data protection, and user trust.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Integration is often the hardest step. Many large organizations still rely on outdated infrastructure that lacks modern APIs. Connecting a chatbot to such systems requires middleware or custom connectors, which can increase both development time and cost. Proper documentation and phased rollout help minimize disruption.
Managing Complex Conversations
Handling nuanced or emotional interactions is another challenge. Even advanced NLP models can misread tone, intent, or sarcasm. In healthcare or customer support, one misunderstanding can lead to misinformation or user frustration. Continuous training, dataset updates, and real-time monitoring are essential to maintain accuracy.
Data Security and Privacy
Data protection is critical. In healthcare, chatbots must comply with HIPAA standards. In Europe, the GDPR enforces strict rules for data handling and user consent. Both frameworks require encryption, role-based access, and audit logs to prevent unauthorized use of sensitive information.
Accuracy and Human Oversight
A chatbot that gives wrong or misleading advice — financial or medical — can cause serious harm and reputational loss. To prevent this, enterprises should apply a “human-in-the-loop” approach, where uncertain or high-risk cases are automatically escalated to a human expert. Regular validation ensures data and responses remain up to date.
Governance and Ethics
Enterprises must also address governance and ethical transparency. Users should always know when they are interacting with an AI system. Ethical design, informed consent, and explainable reasoning help maintain accountability and public trust while aligning with international AI regulations.
The Future of Enterprise Chatbots
The next stage in enterprise chatbot evolution focuses on multimodal interaction, explainable AI, and stronger ethics.
Chatbots will soon process text, voice, and image data together, creating smoother, more human-like conversations. Integration with IoT systems will grow — allowing employees to speak directly to connected devices or retrieve data hands-free.
As speech recognition error rates dropped below 5%, according to the Stanford AI Index Report 2023, voice interfaces are becoming reliable enough for large-scale enterprise use.
Explainable AI (XAI) will become standard. Users and regulators will expect bots to show how they reach decisions. The OECD AI Policy Observatory (2023) found that over 60% of AI governance frameworks now include explainability rules.
Ethical and privacy standards will tighten under initiatives like the EU AI Act (2024 draft). Companies will need to audit their chatbots for fairness and compliance.
Enterprise AI investment grew by 13% last year, with conversational systems among the top three AI use cases, according to the Stanford AI Index Report 2023.
In the coming years, chatbots will become proactive — predicting needs, offering help before users ask, and blending digital communication with real-world context.
Key Takeaways About Enterprise Chatbots
- Enterprise chatbots automate workflows and scale communication.
- They come in three forms: rule-based, AI-powered, and hybrid.
- Benefits include speed, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction.
- Examples like Sephora and Bank of America show real impact.
Ethical use and accurate data handling are essential for success.
FAQ
An AI assistant designed to automate workflows, data processing, and communication in large companies.
Rule-based, AI-powered, and hybrid.
Efficiency, scalability, and better user experience.
Sephora’s virtual assistant and Bank of America’s Erica.
Integration with legacy tools, privacy compliance, and maintaining trust.