Talking to machines is no longer a novelty. It’s normal. In fact, in 2025, 153.5 million Americans are using voice assistants to manage daily tasks like checking the weather, shopping, or making calls. Globally there are 8.4 billion voice assistant devices in use. This explosion in voice-first tech isn’t just about asking Siri to turn off the lights. It’s quietly transforming critical areas like healthcare, customer service, and regulated industries.
The reason is simple. Modern voice AI combines advanced language understanding, contextual memory, and real-time learning. It’s no longer a static tool. It learns, adapts, and becomes a dynamic part of human workflows. Here’s a closer look at how it all fits together, where it’s already being used, and how to avoid common pitfalls when deploying it.

What Is a Conversational AI Voice Agent?
Conversational AI voice agents are systems that let users speak to machines in natural language. These systems don’t just follow commands. They understand context, learn from previous interactions, and deliver meaningful responses.
Unlike scripted bots from a few years ago, today’s agents adjust their replies based on what you say, how you say it, and even when you say it. That’s possible because of Natural Language Processing (NLP), intent detection, and feedback loops built into their architecture.
Platforms like the Graphlogic Generative AI Platform combine all these components with tools like Retrieval-Augmented Generation. That means the agent doesn’t rely only on predefined rules but fetches the most relevant, updated answers from knowledge sources. For industries like healthcare, this can cut down the risk of outdated information.
A well-designed agent can understand different sentence structures, switch between tasks, and even clarify user intent by asking for more information — something traditional rule-based bots cannot do.
Key Tech Under the Hood
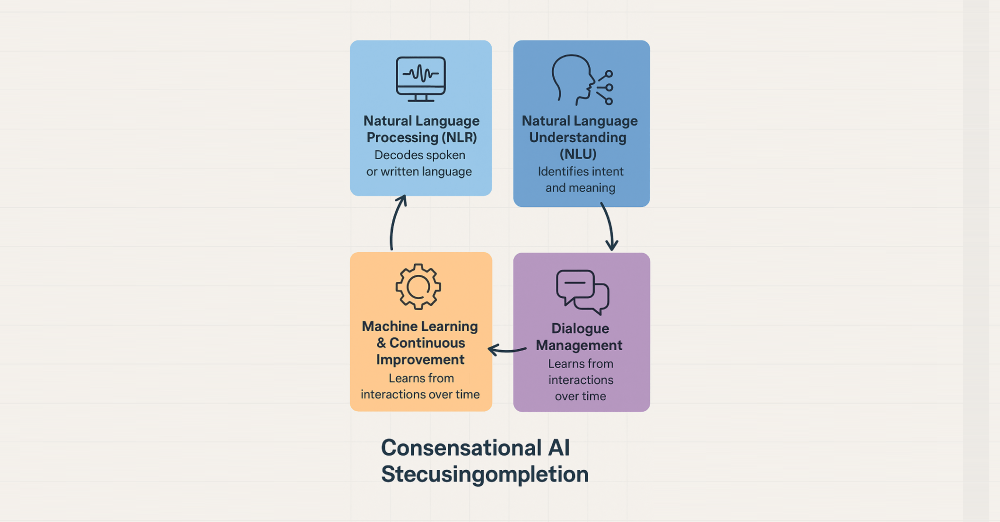
Four main technologies make these agents work:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP helps the system decode spoken or written language. It segments phrases, removes noise, and turns language into machine-readable instructions. This enables real-time transcription, speech-to-text conversion, and content analysis.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU). NLU digs deeper. It identifies what the speaker wants by evaluating intent, tone, and structure. For example, when a patient says “I don’t feel well,” the system learns to ask follow-up questions instead of giving general advice.
- Dialogue Management. This layer keeps the interaction consistent. It ensures the AI stays on topic and refers to previous messages when needed. Without it, conversations would reset every time.
- Machine Learning and Continuous Improvement. The more the agent talks to users, the better it gets. Machine learning algorithms study patterns, analyze what worked, and tweak future responses. This continuous learning improves accuracy and makes the interaction smoother over time.
Top healthcare platforms now use similar logic for virtual nurses and appointment agents, as outlined in reports by Harvard Health and Nature Digital Medicine.
One optional component that’s becoming more common is sentiment analysis. This lets the agent detect stress or dissatisfaction in a person’s voice. While not yet perfect, this tech is helping early mental health bots detect distress or panic in users before escalation.
Where Voice AI Is Already Working
Healthcare
Voice AI is already embedded into hospital systems, telehealth apps, and remote monitoring platforms. It handles appointment reminders, symptom screening, and post-surgery check-ins. The key benefit is that patients can interact using plain language without needing to log into complex apps.
Some hospitals use agents to answer basic pre-op questions, reducing call center loads by 40 percent. Tools like Mayo Clinic’s telemedicine guide show how this helps streamline workflows.
For patients with mobility issues, speech-first interfaces can be the only accessible option. This is especially critical in rural or underserved areas where medical staff availability is limited.
Customer Support
Call centers now integrate AI agents that can triage questions, escalate urgent issues, and log feedback without any human input. Businesses use agents to filter thousands of queries a day, with response time going from hours to seconds.
In multi-language environments, agents use real-time translation alongside speech recognition. That cuts down errors and improves access for non-native speakers.
Finance
Banks and fintech firms use voice bots to verify identities, provide real-time account info, and even walk users through mortgage applications. These bots can flag irregular patterns in speech that may suggest fraud, such as stress or hesitation during security questions.
Reports from JAMA Network highlight how AI improves operational security while enhancing user experience, especially in high-trust sectors.
E-commerce
Retailers use voice agents to guide users through returns, product discovery, and recommendations. Unlike text interfaces, voice allows for quick back-and-forth and less friction when browsing. Personalized shopping suggestions based on past behavior boost conversion rates and retention.
Agents also reduce cart abandonment by helping users at the point of hesitation — just before checkout or after delivery issues.

Types of Voice Agents, Simplified
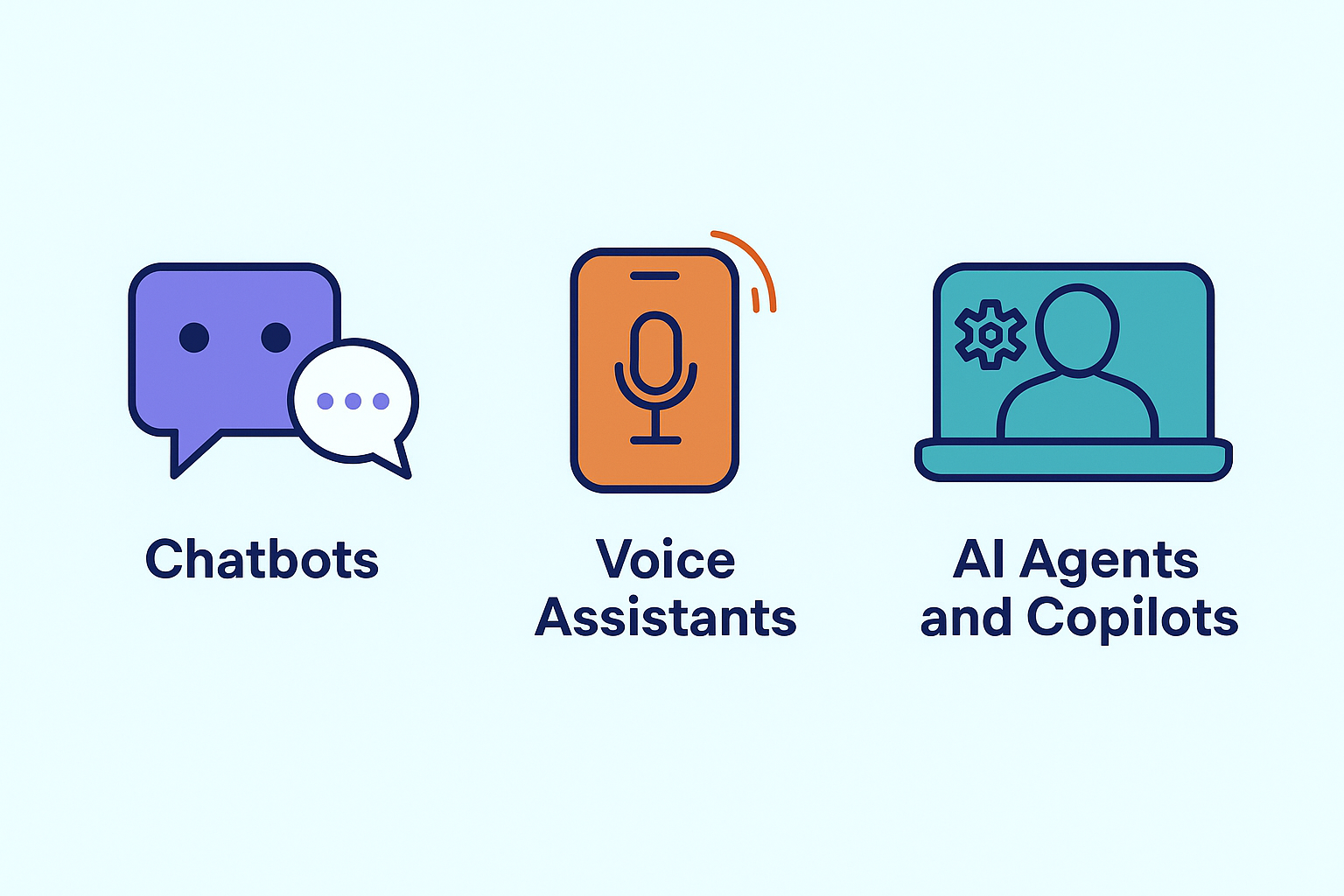
Understanding what kind of agent suits your need is essential. The three core types are:
- Chatbots. These are entry-level tools that work via text or voice, mostly on websites. They’re good for answering FAQs but struggle with follow-ups.
- Voice Assistants. Tools like Siri or Google Assistant can handle simple commands and integrate with phones, smart speakers, or cars. They’re great for hands-free convenience but often lack domain-specific intelligence.
- AI Agents and Copilots. These are advanced systems that manage workflows, remember preferences, and adjust their behavior over time. Platforms like Graphlogic Voice Box API enable this level of interaction across enterprise environments.
Companies often start with chatbots and evolve toward copilots once demand and complexity grow.
The Benefits Are Practical
Voice-first agents can improve business operations and user satisfaction in measurable ways.
- Time savings. AI agents handle basic tasks instantly, reducing the need for human staff in repetitive workflows. This lets teams focus on higher-level decisions.
- Higher customer satisfaction. Because they remember past interactions, AI agents give more personalized replies. They also reduce response time, which boosts satisfaction scores by up to 15 percent, according to McKinsey Digital.
- Better scalability. Unlike human agents, voice AI doesn’t need breaks or shift planning. It can handle traffic spikes without degrading service.
- Cost savings. By automating tier-1 queries, companies cut call center costs. In high-volume industries, this can mean millions in annual savings.
- Consistent tone and message. Voice AI maintains a uniform level of politeness and professionalism, 24 hours a day. This matters in regulated environments where tone must remain neutral and respectful.
But There Are Real Limits
Even the best AI voice agents face major hurdles.
| Challenge | Description | Best Practice |
| Language complexity | Hard to understand accents, slang, sarcasm | Train on diverse speech patterns |
| Privacy & regulation | Voice data is sensitive, must meet HIPAA/GDPR | Use encryption and follow global standards |
| Emotional limitations | Can’t truly detect emotions, relies on tone or phrasing | Avoid in crisis or high-stakes situations |
| Integration difficulty | Needs deep tech changes, API setup, maintenance costs | Start with a pilot before scaling |
Best Practices Before You Deploy Voice AI
Being clear that someone is talking to AI is important because it builds trust and helps set the right expectations. Asking for feedback, even through simple ratings or quick surveys, provides valuable insights into what’s working and what could be improved. Language and user behavior change quickly, so it’s important to keep the model updated using real-world data, not just test environments. Privacy must be a priority, especially when handling voice data in sensitive areas like healthcare or finance, where responsible storage and processing are essential. Choosing reliable partners like Graphlogic can save time and help ensure compliance from the very beginning.
What’s Next?
Multimodal interaction is quickly becoming the norm. Future AI won’t just listen — it will also see and respond visually, which is a big win for users who prefer to read or need a bit of visual confirmation. We’re already seeing this in action with platforms showing charts, maps, or even medical scans right alongside voice responses. Emotional AI is making strides too. New systems are starting to pick up on things like stress, confusion, or urgency, and in healthcare, that’s opening the door to smarter triage and more responsive mental health support. Voice AI is also spreading fast across industries. Schools are using it for tutoring, law firms for contract review, and travel companies to help people plan trips by just talking. What once felt futuristic is now becoming everyday infrastructure.
Final Thought
Voice-first AI is not just about convenience. It’s about creating systems that are more inclusive, faster, and adaptable to real-world needs.
But success comes down to how thoughtfully the tech is deployed. Prioritize transparency, data ethics, and user experience — not just automation. When done right, conversational AI doesn’t replace humans. It helps us do more of what matters.
FAQ
Yes, if properly implemented. Data should be encrypted during transit and storage. Be sure your platform complies with local data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA.
Some systems support multilingual interaction, but accuracy varies. Always test for your target regions and accents before deployment.
Machine learning models benefit from hundreds or thousands of real-world conversations. However, you can start small and train incrementally.
Not always. It depends on context. In healthcare and smart homes, voice is often preferred. In noisy or shared spaces, people still choose text.
You can explore a working example using Graphlogic’s Virtual Avatars demo, which shows how natural voice interaction looks in practice.

